1935 - Bulk blending plant, which was part of GLAVAZOTA People's Commissariat of Heavy Industry, commissioned in June 1935.
1941 - Construction began superphosphate plant using equipment. Work was halted due to the World War.
1942 - 45 During the World War the factory worked to produce defence products. In January 1942, the plant began to produce explosive dinamon "F". The release of this matter lasted until 1945.
1946 - Work on the commissioning of the 1st stage of superphosphate plant was completed on 6 April 1946.
1946 - 47 Start of construction on the sulfuric acid plant in 1946 and its commissioning in September 1947.
1949 - 56 Designing and construction of a new superphosphate plant, equipped with advanced technology design capacity of 250,000 Tons / year, The plant was commissioned in 1956
1953 - Launch of a pilot plant for production of ammoniated super single phosphate
1958 - Launch of captive sulfuric acid production, due to increased capacity of superphosphate in 1956,
1962 - Commissioning of 250,000 tons per year capacity plant for production of ammoniated superphosphate.
1964 - Introduced of enhanced technology of producing ammoniated superphosphate under the new scheme - ammonization - drying - sieving - crushing.
1967 - Installation of two additional ammonization drums.
1971 - Reconstruction of dryers and cyclones with improved technology of self-cleaning device.
1973 - Technology upgradation of equipment relating to handling of rock phosphate powder, additional cooling of superphosphate including additional screening has been completed.
1988 - Capacity reduced to 175,000 tons per year to address ecological issues and to start use of Kyzylkum phosphorite. Since then the plant moved to the processing of local raw material - phosphate rock deposits of raw "Tashkura" which resulted in a recalculation of capacity to 178,000 tons per year of Ammoniated Super Phosphate.
1991 - After the collapse of Soviet Union and resulting collapse of economic ties and the opening of national phosphate deposit in the Navoi region. Djeroy Sardar plant switched to processing of low-grade phosphate rock beats. weight 0.98 g / cm3 with P2O5 content of not less than 16%.
1997 - By order of the State Property Committee of the Republic of Uzbekistan ? 91 of 30.05.1997 year, one of the first in the chemical industry translated into a stock corporation and renamed JSC "Kokand superphosphate plant"
2003 - The general designer of Chirchik "O'ZKIMYOSANOATLOYIHA" was developed by a working project "Reconstruction of ammonization, granulation, drying and classification of ammoniated superphosphate plant." The project provided for the ammonization 12% - aqueous ammonia solution in order to bring the power plant ammonization to 250 thousand tons of granulated superphosphate ammoniated by 2010. Developerprocessof "NIIGIPROHIMNAUKA." Russia, St. Petersburg.
2004 - The reconstruction of ammoniated superphosphate plant for the production of ammoniated superphosphate in granulated form and reduces dust and gas emissions.
2006 - The design capacity increased to 250,000 tons of ammoniated super phosphate in kind. The modernization program technological lines ammoniated superphosphate plant" to improve the particle size distribution of the finished product:
2007 - Started using phosphorite concentrate "Tashkura" of washed dried at TSh 81.2-23: 2006 with the general content of P2O5 (18-19) %.
2015 - Since March 2015 it started use of washed calcined phosphorite concentrate O'zDSt 2825-2014, with the total content of P2O5 (26) %. Since April 2015, This allowed production of superphosphate ammoniated with essential nutrients P2O5 at 20%.
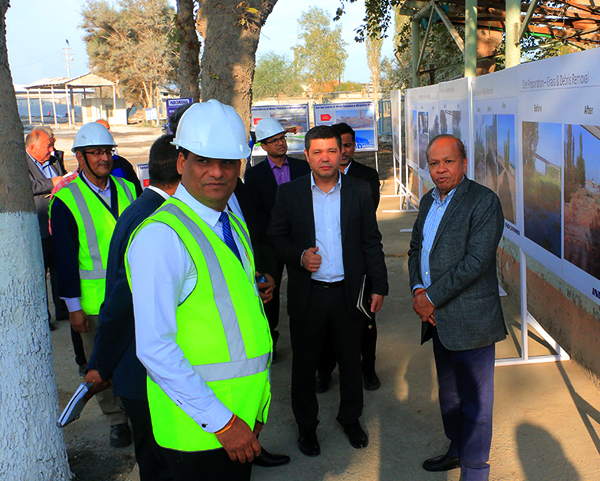
2019 - The government of Uzbekistan initiated a privatisation program under which Indorama Corp. acquired 95.54% of government stake and launched a complete modernisation and turnaround program. The plant is expected to restart in the Q1 2021 with a capacity of 350,000 tons of super phosphate and 290,000 tons of ammoniated super phosphate.



 English
English Uzbek
Uzbek












